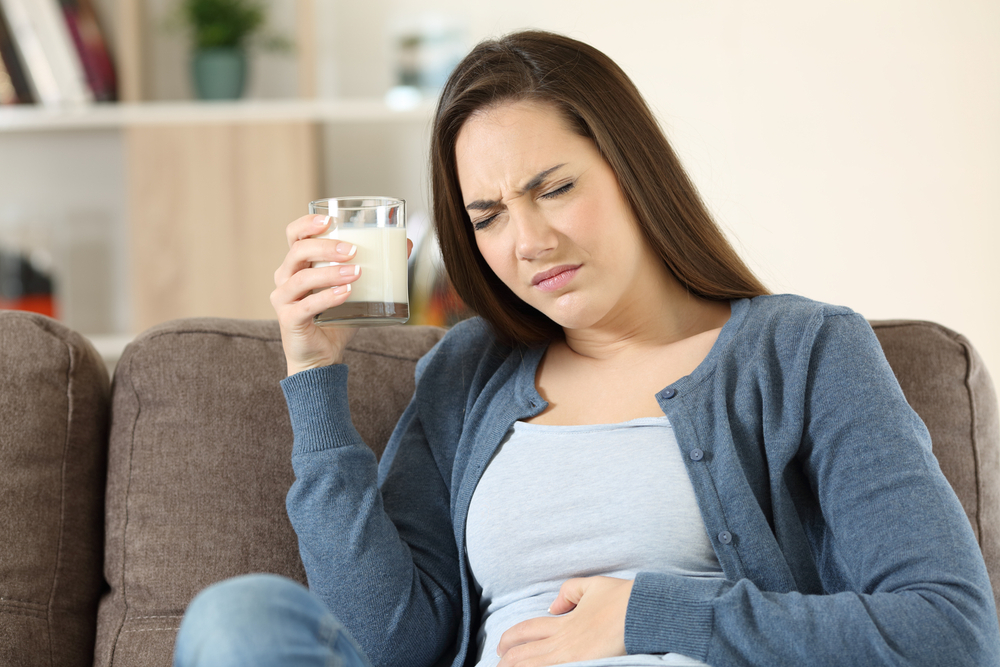
Common Signs of Lactose Intolerance
Dairy products are among the highly consumed food products. Although they are good sources of multiple nutrients, they are not safe for everybody. For instance, people with milk (or casein) allergy or lactose intolerance should avoid milk and milk products. Since the two conditions are common and have many similar symptoms, they are often confused. However, they are totally different.
Milk allergy arises when the immune system reacts against a particular milk component. On the other hand, lactose intolerance is a condition where digestion of the sugar component of milk called lactose is impaired. The impairment is due to the deficiency of an enzyme called lactase. Lactase enzyme deficiency results in lactose indigestion and malabsorption. Consequently, the undigested lactose is passed to the colon, where colonic bacteria break it down. Accordingly, the breakdown process and the breakdown products result in various signs and symptoms:
1. Stomach pain
The breakdown of lactose by gut bacteria results in the release of various gases such as carbon dioxide, hydrogen, and methane. The gases are trapped within the intestines and may push intestinal walls hence, resulting in pain. Besides, the gases can be converted to acid that contributes to the pain. The pain will be felt in the stomach area and will vary in the degree of severity. In case of cramping due to the accumulation of gas, the severity will increase.
2. Diarrhea
The presence of undigested lactose often leads to diarrhea or loose stools. When the undigested sugar ferments, it results in metabolites that have high osmotic potential; hence they draw water from the cells into the lumen of the intestines. Besides, lactose also contributes to the water load drawn, thus increasing stool volume and subsequent diarrhea.
3. Bloating and gas
Malabsorption of lactose is the prime cause of increased gas or bloating. Lactose is a disaccharide. Sometimes disaccharides and complex carbohydrates may cause bloating if they are not digested well. In lactose intolerance, lactose is not digested to simple sugars, galactose, and glucose for absorption in the small intestines. Therefore, its destruction in the large intestine by bacteria causes the production of gas. Consequently, the produced methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide accumulate, leading to discomfort. Remember, the efficiency of your normal flora will determine the amount of gas. Additionally, the gas will be odorless since it is due to carbohydrate breakdown and not protein breakdown.
4. Constipation
One of the gaseous products during lactose breakdown in the colon is methane gas. The gas has various effects, including impairing gastric motility. Thus, the transit time for food is increased as it moves slowly along the gut.
5. Headache
Headache is a common constitutional symptom. In lactose intolerance, headache may be due to the close connection between the gut and the brain. Besides, any systemic illness or disturbance can cause headaches.
6. Mouth ulcers
Dairy products or milk can cause canker sores or mouth ulcers. The sores can be excruciating. However, they occur rarely, and in some cases, they may be associated with allergies to milk or milk products.
Lactose intolerance is a fairly common condition. Although it is not dangerous, it is very uncomfortable. Interestingly, it can be easily managed to prevent any related complications and the accompanying discomfort.