5 Complications of Ovarian Cancer
Often known as the “silent killer”, ovarian cancer rarely has any symptoms. It is only when the disease progresses that symptoms show up. Moreover, advance stages of ovarian cancer bring along certain health complications as well. These complications generally arise from metastases in the lungs and abdomen.
While everyone may not experience these complications, it is always advisable to be aware about them. In this vein, listed below are five common complications of ovarian cancer:
1. Perforations in the colon
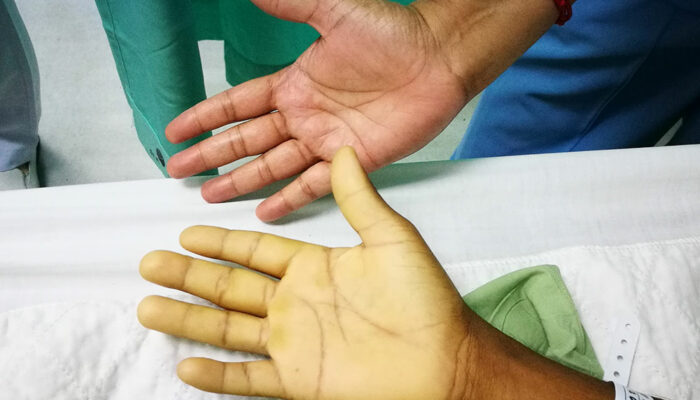
Sometimes, the malignant cells can metastasize along the walls of the intestines. The tissues along the lining of the intestines will become weaker over time. As a result, perforations may form in the colon. This causes the contents of the bowel to leak inside the abdominal cavity, which, may, in turn, lead to infections. Surgery is required to treat severe cases.
2. Bone pain
In some cases, the metastases from ovarian cancer may develop in the bones as well. In such cases, bone pain is inevitable. However, this complication is avoidable. Bone-modifying medications are often prescribed to avoid this complication. Radiation therapy has also been useful in managing and avoiding bone pain.
3. Pleural effusion
This complication develops due to metastases in the chest area or the lungs. It causes fluid buildup in the membranes (pleura) that line the lungs. The fluid may even contain cancer cells, in which case the condition is known as malignant pleural effusion. This complication can be remedied with a process known as thoracentesis. A needle is inserted in into the pleural cavity to drain out the fluid.
4. Bowel obstruction
Bowel obstruction is a complication that arises due to the development of metastases in the pelvic or abdominal region. Sometimes, scar tissue formed after pelvic or abdominal surgery may also lead to bowel obstruction. Adhesions formed after ovarian cancer surgery may also cause this complication. The adhesions or scar tissue may cause the buildup of twists or kinks in the bowel system, which causes obstructions to the smooth flow of the contents of the bowel. This can cause severe pain and cramps in the abdomen. Some may also experience nausea and vomiting. Surgery is prescribed to manage severe bowel obstruction.
5. Urinary retention
In some cases, ovarian cancer cells can travel to the pelvic region. These cancerous cells block the ureters, which are the tubes connecting the bladder and kidneys. When both the ureters are blocked, there will be minimal to zero urine flowing out of the body. In case only one of the ureters is blocked, a person may experience severe pain in the pelvic region. Often, catheters are used to clear up the blockage.